This IBM® Redbooks® Solution Guide provides a high-level overview of the IBM Intelligent Operations Center V1.6.0.1 programming model and extension points that developers can use to customize the solution for the target environment.
IBM Intelligent Operations Center includes an application-based programming model that supports all the interactions with the solution components. The programming model is based on the industry standards Representational State Transfer (REST) and Java technologies. IBM Intelligent Operations Center includes a full set of REST and Java APIs that provide a simplified development environment and make the platform easy to extend and customize for a large community of developers. The services that are provided with IBM Intelligent Operations Center enable access to the data in the database, and the capability to process the data and act on it. The services can be accessed from client-side code through the REST service interface and from server-side code through the Java APIs.
IBM Intelligent Operations Center provides the base platform for IBM and IBM Business Partners to build end-to-end solutions for various domains. IBM Intelligent Operations Center can be extended and customized by using either line of business (LOB) configuration tools that do not require programming skills, or the REST and Java services and extension points that are part of the programming model (see Figure 1).
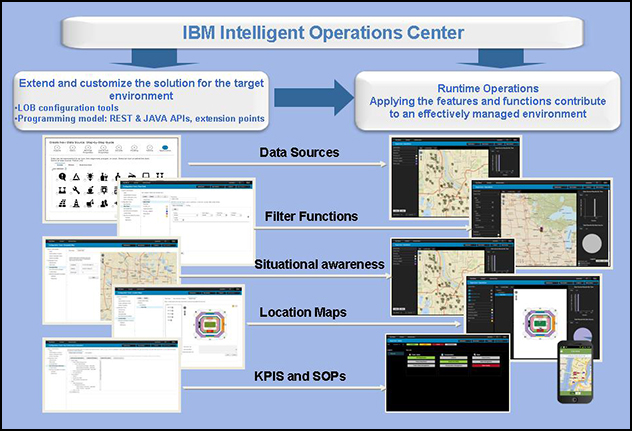
Figure 1. Extending and customizing the end-to-end solution for the target environment
Did you know?
Today, most people around the world live in urban areas. In the years to come, the percentage of people who are living in cities will continue to rise with the population. By 2050, two-thirds of the world’s population will live in cities.
Citizens and businesses are placing increasing demands on leaders to innovate to progress. People are becoming increasingly more connected through social media, and massive amounts of new data are created every day. As a result, leaders are forced to determine ways to harness and drive insight and actions from the information that they have available to create more value for their citizens, drive sustainability, and enhance the quality of life.
Open API adoption, especially REST-based interfaces, has grown dramatically in the last couple of years, allowing a large community of users and developers to identify new uses for existing data and infrastructure.
Business value
Platform APIs and extension points enhance the value of the end-to-end solution by promoting co-innovation and new ways to use the platform's capabilities. The IBM Intelligent Operations Center programming model provides flexibility in implementing new capabilities that improve the user's experience, productivity, and time-to-value.
Based on popular technologies (REST and Java services) and built-in configuration tools, the IBM Intelligent Operations Center programming model enables a large community of developers and business users to rapidly extend and customize the base solution to meet domain-specific needs.
In addition, the IBM Intelligent Operations Center solution provides the following business benefits:
- Provides a city services request management system with executive, city operations, and agency dashboards that include domain KPI reports with trends and analysis of event and domain data.
- Helps city officials to better monitor and manage city services by providing them insight into daily city operations through centralized management and data intelligence.
- Allows different data sources to be synergized together to provide clear and accurate information about domain operations.
- Helps city agencies to prepare for problems before they arise and to coordinate and manage problems when they do arise.
- Enables officials to communicate instantly and to discuss and synchronize rescue efforts so that they can send the right people and equipment to the right place at the right time.
- Provides drill-down capabilities about details of service requests, team members, assets that are assigned, and status, which is also available in a geospatial context for situational awareness.
- Facilitates cross-agency decision making, convergence of domains, coordination of events, communication, and collaboration, which improves the quality of services to citizens and reduces expenses.
- Automatically flags event conflicts between city agencies.
- Optimizes planned and unplanned operations by using a holistic reporting and monitoring approach.
- Helps operations executives or staff to adjust systems to achieve results that are based on the insights that are gained.
Solution overview
The IBM Intelligent Operations Center programming model includes a set of services and extension points. The services provide a standard way to access the data, both from client-side code (through the REST interfaces) and from server-side code (through the Java interface). The high-level design of the IBM Intelligent Operations Center service API is shown in Figure 2.
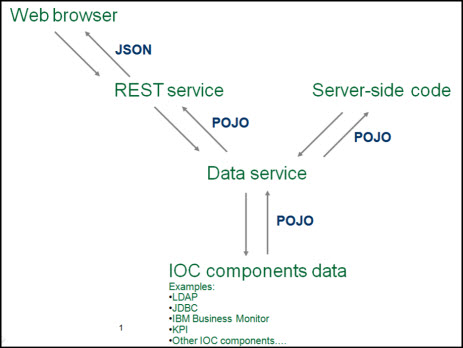
Figure 2. IBM Intelligent Operations Center service API design
In this design, the plain old Java object (POJO) classes transport the incoming parameters and any outgoing result. The same POJO classes are used throughout the design and consist primarily of attributes, getter and setter methods, and a few additional helper methods. The design specifies a data service class. The data service class hides the underlying implementation that is used to interact with the actual data. The underlying implementation could be JDBC, LDAP, or some other non-database API.
Here are some of the main characteristics of these services:
- Results are returned to the REST service as a JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) object (as a POJO to the Java API), but is extensible, so other formats, such as XML, can be supported in the future.
- The REST services follow industry coding standards for REST services. For a list of supported standards, see "IBM Intelligent Operations Center REST interface", found at:
http://pic.dhe.ibm.com/infocenter/cities/v1r6m0/topic/com.ibm.ioc.doc/rest_overview.html
For IBM Intelligent Operations Center REST interface reference documentation, see IBM Intelligent Operations Center V1.6 REST APIs, found at:
http://www-01.ibm.com/support/docview.wss?uid=swg27039957
- The Java APIs provide a standardized way to access the data from server-side code without writing low-level JDBC code. For information about the Java API, see "IBM Intelligent Operations Center Java API documentation", found at: http://pic.dhe.ibm.com/infocenter/cities/v1r6m0/topic/com.ibm.ioc.doc/javadoc/overview-summary.htm
- A set of standardized exceptions is also provided.
The IBM Intelligent Operations Center programming model provides several extension points that allow IBM Business Partners and IBM domain teams to extend the base product. Table 1 lists the main extension points. For more information about the available extension points and implementation examples, see the IBM Redbooks publication
IBM Intelligent Operations Center 1.6 Programming Guide, SG24-8201.
Table 1. Principal IBM Intelligent Operations Center extension points
| Extension point | Description |
| External service URL | This extension point allows you to show data from external system or third-party applications in the IBM Intelligent Operations Center user interface. When the data in an external system cannot be brought into the IBM Intelligent Operations Center because it is not in the standard form, or because of other reasons, a service can be created to pull in data from that data source in the GeoJSON format. The URL for such a service is referred to as external Service URL. |
| Extension properties | This extension point allows you to store more complex data in special properties in the data items from the data sources. |
| Routing expression | For the data that is received from a data source, routing expressions define how the data is processed by the solution. Data items that match the required expression or combination of expressions are routed to the selected destination. |
| Integration topic | This integration point enables the routing of data items to an external system through a routing mechanism. This mechanism directs the data item fulfilling the filter criteria that is specified in a data source routing expression to a predefined integration topic. |
| Custom data source actions | This extension point provides the capability to add actions to the More Actions menu in the preview card for all associated data items. Such an action can provide the function to integrate with a third-party system, or to extend existing product functions. |
| Content panel customization | By default, the content panel has three tabs: Map, Location map, and List. Through customization, you can change the order of these tabs and add or remove custom tabs. Customizing the content panel is useful for integrating with external systems with a web user interface or a custom widget that interacts with or represents data from the REST services in alternative ways. The content panel is implemented through the content viewer portlet, which allows you to create tabs and load custom Dojo widgets inside them. |
| Custom filter-driven results charts | This customization option allows you to add Dojo widgets and provide alternative data visualization. |
| Preview card customization | By default, all the properties for data items in preview cards are in text format. It is possible to add other types of information, such as images, links, or even video. |
Custom portal pages, labels,
and themes. | Creating custom portal pages allows you to customize the user interface for a new user role or provide new functions with custom portlets. This is a standard feature that is provided by IBM WebSphere® Portal. Three custom portal themes are included with IBM Intelligent Operations Center: IOC Portal 8 Admin, IOC Portal 8 Theme, and IOC Portal 8 Reports Theme. A label is used to contain multiple labels or pages and typically does not have any actual content. IBM Intelligent Operations Center navigation is built on two base labels: ioc.Home and ioc.SolutionAdministration. Pages that are created outside of these two labels are not added to navigation. |
| Custom portlets | The user interface of IBM Intelligent Operations Center can be extended by custom portlets. Developers can use the following services to optimize user experience and performance:
- RestStore JavaScript class for accessing REST services
- Translation service
|
| Translation service | The translation service is used to store user interface labels and other displayed text in different languages. It renders the text in to the appropriate language based on the preferred user locale. |
| Custom help links | This customization option allows you to provide documentation for a new custom feature and makes it easily accessible from the standard Help menu. |
| More Actions menu customization | This customization option allows you to add or remove options in the More Actions at the upper right corner of the Operations view. For example, it is possible to call a custom web form or add data into a custom portlet or widget. |
| SOP REST service activity | The REST activity that creates a REST service call to access an external entity. It can also be used to connect a standard operating procedure (SOP) to another SOP running on a different IBM Intelligent Operations Center. |
| Map and location map Dojo topics | IBM Intelligent Operations Center provides maps extension points that allow developers to integrate with the map views and control it. The extension points are available as Dojo topics. |
| RestStore | The RestStore Dojo class provides a consistent way to access REST services, consistent error handling, and polling capabilities, makes the user interface more responsive, and decreases load on the server and network. |
| Session persistence | Use the session service to save settings that are relevant to IBM Intelligent Operations Center users across sessions. The different IBM Intelligent Operations Center components track changes that a user makes to the user interface and various other settings, and persists the changes. |
| Filter pane customization | The filter panel is used to filter the data source data items that are displayed on the map, location map, list, and charts. Data sources can be grouped under a category and displayed together on a filter pane. You can configure filter panes with the filter panel tool. The filter service (base URI /ioc/api/filter-service) can be used to get, create, update, and delete resources that are used to configure filter panes programmatically. The equivalent server-side components are also available in the package com.ibm.ioc.filter in the ioc.jar file. A set of Dojo topics is also available to indicate changes that occur in the filter panel. |
| IBM Cognos® reports | Cognos reports provide additional ways to visualize the data in the IBM Intelligent Operations Center system, enabling business users to analyze the data and make business decisions. |
Solution architecture
IBM Intelligent Operations Center 1.6 supports three deployment options:
- Base or standard edition
- High availability edition
- Extended edition
For more information about IBM Intelligent Operations Center topologies, see the IBM Redbooks publication
IBM Intelligent Operations Center 1.5 to 1.6 Migration Guide, SG24-8202.
Essential integration points for IBM Intelligent Operations Center are provided by the core components: IBM WebSphere Portal, IBM WebSphere Application Server, IBM Business Monitor, and IBM DB2®. The IBM Intelligent Operations Center data ingestion process allows you to pull information from tables and
.csv files. Data can also be acquired from CAP messages through a push mechanism. The REST APIs can be used to push information into IBM Intelligent Operations Center.
Figure 3 shows the architecture of the IBM Intelligent Operations Center solution imposed over the standard edition topology.
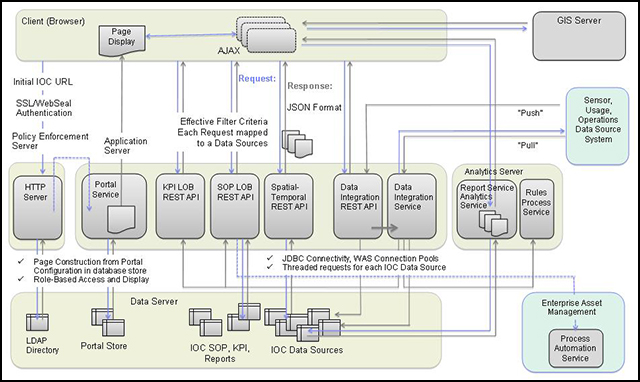
Figure 3. IBM Intelligent Operations Center solution request/response flow architecture
Usage scenarios
Solutions that are based on IBM Intelligent Operations Center expand a broad range of industries and organizations. Several use cases apply to water management, public safety, transportation, social programs, entertainment venues, buildings, energy, and so on.
Figure 4 shows some of the solutions in the IBM Smarter Cities® portfolio that are built on IBM Intelligent Operations Center. As described in this Solution Guide, the IBM Intelligent Operations Center programming model enables a large global business partner ecosystem to build solutions by extending and customizing the base platform.
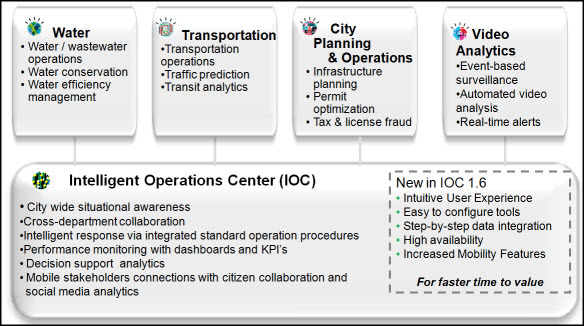
Figure 4. IBM Smarter Cities solutions built on IBM Intelligent Operations Center
The following sections give examples of IBM Intelligent Operations Center usage scenarios.
Advanced emergency response system
In this scenario, IBM Intelligent Operations Center is used to build a city’s advanced emergency response system. The city’s operations center integrates information and processes from many city agencies into a single operations center that provides a holistic view of how the city is functioning on a 24x7 basis.
In this case, a city wants to improve its safety and responsiveness to various incidents, such as flash floods and landslides. The solution is to create an automated alert system that notifies city officials and emergency personnel when changes occur in the flood and landslide forecast for the city, based on predefined thresholds. Contrary to previous systems in which notifications were manually relayed, the new alert system is expected to reduce the reaction times to emergency situations. It uses instantaneous mobile communications, including automated email notifications and instant messaging, to reach emergency personnel and citizens.
The emergency management solution, which is based on IBM Intelligent Operations Center, offers the following advantages:
- Integrates information from across agencies and systems.
- Provides a dashboard to manage and visualize workflows.
- Facilitates cross-agency decision making and collaboration.
- Optimizes intra-agency resource and task scheduling.
- Automatically flags event conflicts between city agencies.
- Efficiently controls and uses cross-agency resources, reducing the time to resolution of emergency and crisis situations.
The emergency response system, which is based on IBM Intelligent Operations Center, has the following benefits:
- Helps to save lives by enabling city officials to react and respond to disasters faster and more efficiently.
- Maximizes efficiency and improves service levels that are provided to citizens.
Wastewater management
With the IBM Intelligent Operations Center acting as the central point of command, the solution collects, analyzes, and monitors live data from sensors and level indicators in the sewer system. It also helps control wet weather flow through the remote use of wireless sensors, smart valves and ballasts, or inflatable bands.
A city’s department of water works utility maintains a complex system of water mains, water meters, filtration plants, well fields, and water storage facilities. The system uses a combined sewer overflow model in which one large pipe carries all waste water, storm water, sanitary sewage, and other pollutants to the water treatment plants. In a heavy rainstorm, the city’s aging infrastructure cannot handle the large volumes of rainwater and waste water. The resulting overflow of raw sewage never reached the treatment plants and, instead, was released directly into the river, posing significant health and property risks.
City officials were looking for a way to solve this problem, but to further extend and use the water system’s existing data and sensor technology. They were looking for a more sophisticated and intelligent alternative to digging up the city’s streets and rebuilding virtually the entire water works infrastructure.
A solution that is based on IBM Intelligent Operations Center collects information from sensors that are placed in the sewer system. These sensors proactively monitor and alert the city water authority when water is rising to dangerous levels or a blockage occurs. This sensor data can then be used to create a dashboard with geospatial mapping, showing precise "hotspots" where a risk of sewage overflow is greatest.
The solution has the following key features and capabilities:
- Overlay mapping of key data values for at-a-glance status
- Collection system for wastewater levels and pumping station operation
- Collection of trending and historical data from water and wastewater operations for planning
- Basement backup heat map
- Calculation of combined sewer overflow volumes from supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) collection system wastewater levels
- System-level and geographic information system view of cross-silo SCADA components
The solution relies on data that is collected by sensors and integration of software that is provided by IBM Business Partners. This integration is possible thanks to IBM Intelligent Operations Center architecture and programming model.
By implementing this solution, the city can make proactive decisions, and initiate and monitor predefined action plans to alleviate or manage a flood threat. City operators can take proactive measures, such as deploying a crew to repair a sewer line; call in fire, police, or rescue personnel; or send an urgent alert to citizens to prevent public health disasters before they occur.
The solution helps the city to attain real business results:
- Cut wet weather overflows and dry weather overflows.
- Gain millions gallons of capacity in its water system
- Avoid millions of dollars in infrastructure investments plus more in potential government fines.
In addition to collecting and aggregating data to deliver a unified view of the combined sewer overflow infrastructure, the solution employs sophisticated analytics and monitoring capabilities that help the city predict where sewage overflow is likely to occur.
Integration
IBM Intelligent Operations Center can be integrated with other systems to share data, and visualize and act on events. There are several ways in which integration with external systems can be implemented:
- Integration through standard operating procedures (SOPs):
- Integrating with IBM SmartCloud® Control Desk through the Automation Activity type in an SOP
- Integrating with external systems through the REST Activity type in an SOP
- Using a data source routing expression to direct events to a predefined integration topic. External applications listening on the topic can pick the events up for processing.
- Using a service URL on the data source REST service to pull in data from external systems for visualization on the map or list views.
- Using server-side Java services.
- Creating a custom data source action from the preview card.
For detailed information about the options that are available for integration with external systems and implementation examples, see Chapter 9, "Integrating with external systems", in
IBM Intelligent Operations Center 1.6 Programming Guide, SG24-8201.
Supported platforms
IBM Intelligent Operations Center can be deployed within a city's data center (on-premises) and it is also available through a subscription service with IBM Intelligent Operations Center for Cloud, which is a Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solution.
For city managers that prefer a subscription service model that does not require additional hardware or IT management capacity, IBM Intelligent Operations Center for Cloud is an ideal solution. This service provides rapid and secure Internet access to the capabilities of the IBM Intelligent Operations Center on an IBM Cloud. IBM Intelligent Operations Center for Cloud offers a straightforward, user-based subscription service at a single price that includes all costs, including hardware, software, maintenance, support, and networking. It is built on the same key technologies as the traditional software, and is managed by IBM delivery teams to lower the total cost of ownership (TCO). For more information, see "IBM Smarter City Solutions on Cloud", found at:
http://www.ibm.com/software/industry/smartercities-on-cloud
For on-premises deployments, IBM Intelligent Operations Center standard topology requires four servers with Intel x86-64 or AMD x86-64 processors. Eight servers are required for the high availability topology. Red Hat Enterprise Server Linux version 6 at release 6.3 or higher plus specific Linux RPM packages must be installed on the servers. For information about minimum hardware requirements, see
"IBM Intelligent Operations Center hardware requirements for a standard environment", found at
http://pic.dhe.ibm.com/infocenter/cities/v1r6m0/topic/com.ibm.ioc.doc/ba_plan_hardware_lite.html, and "IBM Intelligent Operations Center hardware requirements for a high availability environment", found at
http://pic.dhe.ibm.com/infocenter/cities/v1r6m0/topic/com.ibm.ioc.doc/ba_plan_hardware_advanced.html. For information about prerequisite software, see "Prerequisite software requirements", found at
http://pic.dhe.ibm.com/infocenter/cities/v1r6m0/topic/com.ibm.ioc.doc/ba_plan_server_software.html.
Ordering information
IBM Intelligent Operations Center is available only through IBM Passport Advantage®. It is not available as a shrink-wrapped product. This product has the following ordering details:
- Product Group: Smarter Physical Infrastructure
- Product identifier: 5725-D69
- Product identifier description: IBM Intelligent Operations Center
- Product Category: IBM Smarter Cities
- Charge metric: User Value Unit (UVU)
Ordering information is shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Ordering part numbers and feature codes
| Program name | PID number | Charge unit description |
IBM Intelligent Operations Center | 5725-D69 | Charge metric: User Value Unit (UVU) |
Related information
For more information, see the following documents:



